Last updated April 2024
What is skin pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation occurs through the production of melanin in pigment-producing cells, otherwise known as melanocytes. The number of melanocytes present in our skin determines its colour, so those with a lower amount will have lighter skin tones, and those with more will have darker skin types.
However, sometimes pigmentation does not create an even skin tone. When there is an excessive amount of melanin in a particular area, hyperpigmentation occurs. This results in the appearance of darker skin, which can be in the form of freckles, age spots, sun spots, and other skin conditions.
This page will discuss skin pigmentation and its treatment. This discussion will only encompass pigmentation that is in the skin, and will not involve discussion of raised pigmented lesions, moles, or skin cancers.
What causes skin pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation or hyperpigmentation is usually caused by excessive melanin production. This production typically occurs in a limited area due to the clumping of melanin, creating the appearance of brown or darker spots of pigmentation in the skin.
Reasons for skin pigmentation include:
- UV radiation: In most cases, especially in areas with high UV radiation levels like Australia, skin pigmentation problems can be caused by excessive sun exposure. The sun’s rays contain harmful UV light, creating skin conditions like age spots or unwanted pigmentation.
- Hormonal: Conditions such as melasma or chloasma are types of pigmentation typically caused by pregnancy, the pill, or other hormonal influences. This causes changes to patches of skin colour that typically require professional hyperpigmentation treatments.
- Trauma to the skin: Pigmentation can be a result of physical trauma to the skin, such as through improperly done chemical peels and laser treatments, or acne. This is known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, and when left untreated can cause acne scarring or uneven skin quality.
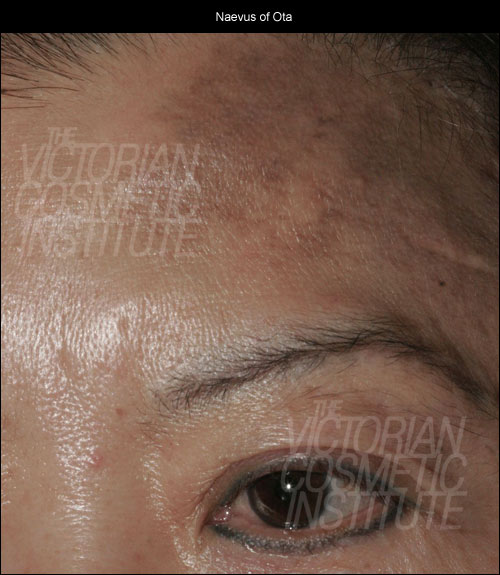
- Birthmarks and acquired pigmentation: Some types of pigmentation can be present from birth, such as birthmarks, or appear suddenly in childhood or adulthood. Examples of these include; congenital melanocytic nevus, cafe au lait spots, spilus nevus, hori’s macules, and nevus of ota. Most of which require laser pigmentation removal to return affected areas to an even skin tone.
Types of pigmentation
There are various types of pigmentation, requiring their own unique form of treatment due to the differing causes and levels of pigmentation. Ultimately, however, skin pigmentation can be categorised into three categories;
- Epidermal (superficial) pigmentation: These pigmentation types are usually close to the surface of the skin and are induced by excessive sun exposure. This type includes solar lentigos, freckles, and cafe-au-lait macules.
- Dermal (deep) pigmentation: Typically found in the dermal layers, these pigmentations include hori’s macules and nevus of ota.
- Mixed dermal/epidermal pigmentation: As a mixed type, these pigmentation traverse through both the superficial and deeper layers of the skin. Melasma is an example of this.
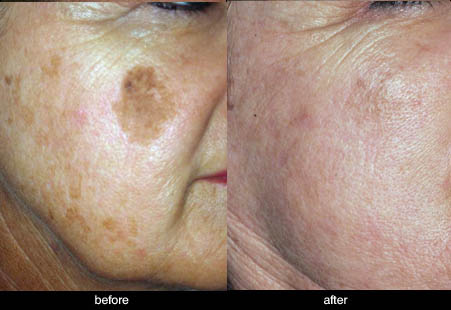
Solar lentigos or sun spots
Most of the common types of pigmentation are caused by sun damage to the skin, and the solar lentigos, colloquially known as ‘sun spots’, are an example of this. Solar lentigos are not cancerous and form on the epidermal layer of the skin. Appearing as flat, brown, ‘muddy’ patches on the areas of skin, these spots typically arise in areas that are more exposed to the sun. Thus, they commonly occur on the cheeks, temples, and forehead.
Seborrhoeic Keratosis
Seborrhoeic keratosis are brown, wart-like growths on the skin. They are benign growths that typically arise from the ageing process and can appear across the entire body on the mixed dermal layer.
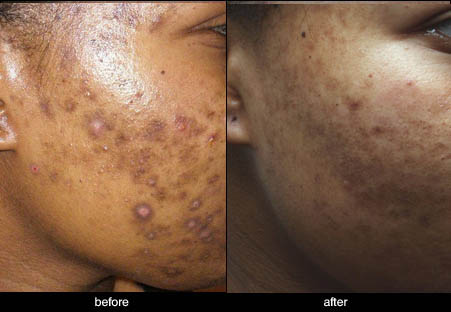
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is a temporary change in pigmentation caused by trauma to the skin, with inflammation also appearing at the affected site. Darker skin is more commonly affected by this condition, but all skin types experience it on the mixed dermal and epidermal layers.
The most common causes of post-inflammatory trauma include:
- Acne
- Laser treatments
- Laser hair removal
- IPL
- Chemical peels
- Physical trauma
In the case of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, it is important to note that treatment of this type of pigmentation can be worsened if further irritation is caused. Thus, treatment of this skin condition requires forethought and professional assessment.
Melasma/Chloasma
Melasma, also known as chloasma, is a form of pigmentation that is stimulated by oestrogen, either from pregnancy, the pill, or normal circulating oestrogens. It appears as brown-grey patches on the face, usually on the cheeks, between the brows and on the upper lip. The skin condition is contained to the mixed dermal and epidermal layers.
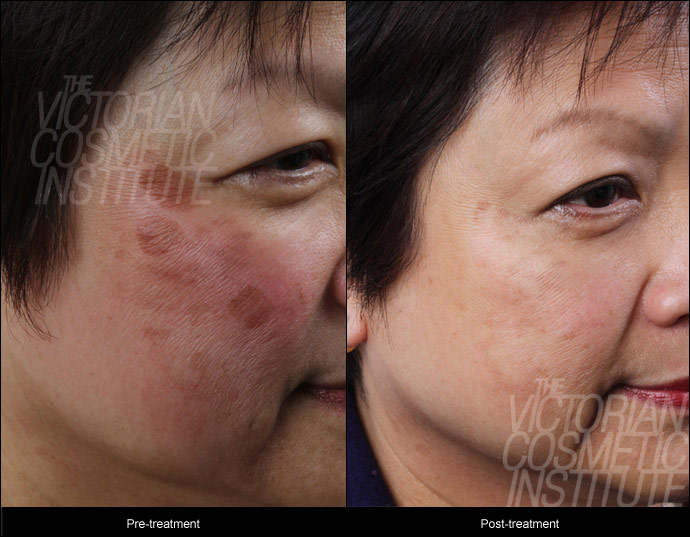
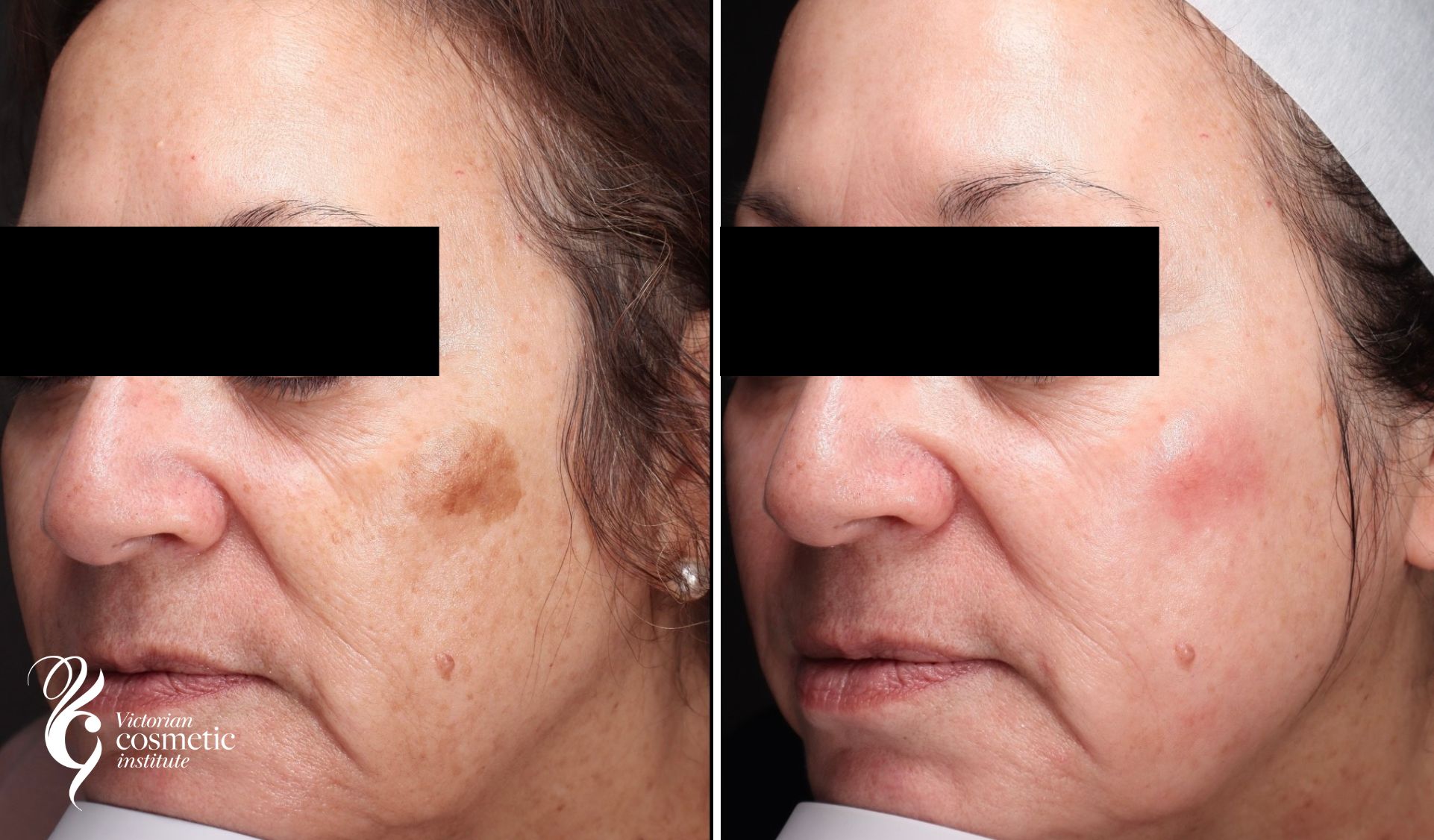
The following pictures show some examples of treatment results at the Victorian Cosmetic Institute:
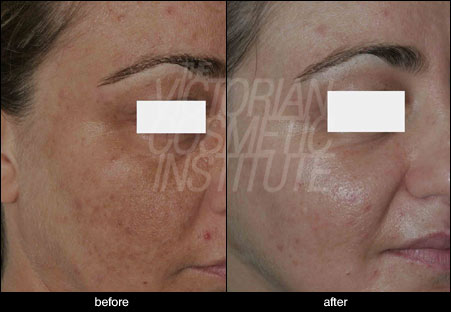
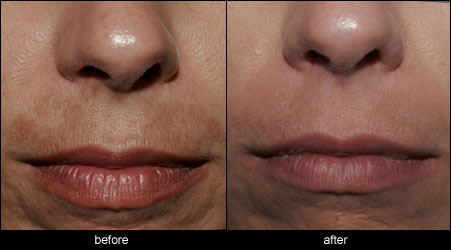
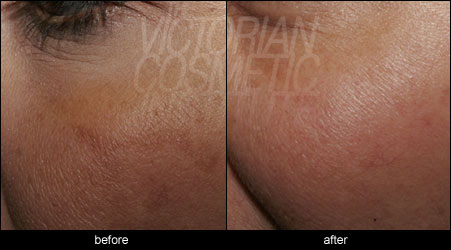
All procedures carry a risk of side effects and potential complications. The outcome of each procedure cannot be guaranteed, and individual results may vary. A consultation with one of our practitioners is required prior to any procedure to assess suitability for treatment. Patient consent has been obtained to display images.
Freckles
Freckles are small brown spots on the epidermal layer of the skin that tend to be more prominent in summer and fade slightly in the winter. This is because freckles are typically genetic and darkened through sun exposure. The brown spots are usually less than 3mm in diameter, with their colouration caused by pigment melanin.
Brown birthmarks
Brown birthmarks, otherwise known as cafe-au-lait spots, are not uncommon and can appear anywhere on the body in the epidermal layers. These spots can be of different sizes and shapes, often ranging in colouration from light to dark brown.
How to treat skin pigmentation
One commonly known skin pigmentation treatment to effectively reduce the appearance of most types skin pigmentation is lasers. However, there are varieties within this treatment, and other potential methods, that are chosen based on the area of concern or skin types requiring treatment. Particularly as there are some risks associated with lasers, such as the loss of normal skin pigmentation (hyperpigmentation), or the rare chance of scarring.
Ultimately, pigmentation can be treated on the face, neck, and decolletage with the following treatments.
Skin treatments
There are various professional and non-invasive treatment options to choose from when looking to reduce the appearance of pigmentation in the skin. The following treatments are effective in improving overall skin tone, even as they target specific skin conditions.
Chemical peels
A chemical peel is an effective method of exfoliating the top layer of the skin, effectively removing dead skin cells and promoting regeneration. This stimulated regeneration encourages collagen remodelling, thus improving the appearance of pigmentation and other blemishes, including:
- Sun damage
- Wrinkles
- Skin texture
- Uneven skin tone
By breaking down excess melanin in the skin and promoting a rejuvenated appearance, chemical peels effectively remove signs of hyperpigmentation. The various chemical peels available, ranging from Alpha Hydroxy acids to Retinoic acids, provide different intensities that can resolve several types of pigmentation.
The Cosmelan Peel Program is recommended for pigmentation concerns such as melasma, sun damage, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and freckles. Cosmelan is suitable for all skin types and much like the Cosmo Peel Forte or Mela Peel Forte, encourages skin renewal for the reduction of various skin conditions. The choice in which chemical peel to use is often determined by personal preference, but their effectiveness on a specific condition is also crucial to consider.
IPL
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) skin rejuvenation is a non-invasive treatment option for pigmentation removal, targeting affected areas with light therapy. The combined application of light and heat is absorbed by pigmented skin cells, causing them to break down and be naturally removed from the skin.
Due to the fact that the level of light energy in an IPL can be adjusted for different layers of the skin, this treatment can be used on multiple pigmentation concerns. However, it is not suitable for small spot treatments due to its intensity. Rather, it is better suited for the overall treatment of the face and/or neck and decolletage.
Gemini laser
When it comes to laser technology, the Gemini laser is one of the more versatile options. While the light of the laser treatment is commonly used for vascular conditions, it can also improve pigmentation concerns such as freckles, seborrhoiec keratosis, and dermatosis papulosa nigra.
The light from the Gemini laser treatment is absorbed by the skin’s melanin, which eventually breaks down the excess and clears the skin from pigmentation. It is particularly effective against Asian, olive, or darker skin tones, showcasing Gemini laser as the versatile choice.
Ruby laser
The name of Ruby laser arises from this treatment’s usage of red light, which is emitted in short bursts to remove pigmentation. The deeper penetration of this treatment when compared to others makes it a better option for pigmentation issues that lie below the epidermal layer. This includes birthmarks, freckles, sun damage, and more.
When the treatment area is targeted by this laser energy, the melanin attracts the light, allowing for the breakdown of pigmentation. Optimal results may also require a stronger or longer amount of light therapy.
Fraxel laser
The Fraxel laser is the first ‘fractional’ laser made to treat several skin concerns, including freckles, sun damage, and hyperpigmentation. The fractional lasers allow for a greater range of skin types to be treated, with the varied wavelengths of light capable of treating epidermal and mixed dermal pigmentations.
The laser is also known to stimulate collagen production, leaving the skin tone even and bright with the removal of dark spots.
Skincare
Although professional and laser treatment are effective means of pigmentation removal, cosmeceutical skincare is also beneficial in reducing the appearance of pigmentation and for maintaining the longevity of your in clinic treatments.
The most crucial step for reducing the appearance of pigmentation is being proactive through regular sunscreen application. Sun exposure is a major contributor to most pigmentation conditions, hence why sun protection should be applied every day, regardless of weather conditions.
If pigmentation already exists within the skin, many types can be treated with specific skincare for pigmentation. When used with sunscreen, these skin-lightening agents reduce pigmentation by inhibiting enzymes that produce melanin, while also increasing the turnover of the skin. Pigmentation serums can also reduce the appearance of dark spots, while also brightening dull skin.
With the addition of vitamin B skincare, which inhibits melanosome transfer to reduce melanin concentration on the skin, skincare can effectively reduce signs of acne scars and hyperpigmentation.
Pigmentation on Asian, olive, or dark skin
Those who are Asian, or have olive or darker skin, tend to develop unwanted pigmentation more than those with lighter skin tones. However, these darker tones tend to require different approaches for laser or light therapy due to their higher levels of melanin.
Additional concerns about adverse reactions for these skin types are also prevalent, such as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation following laser therapy. This side effect may result in the original pigmentation problem seeming worse initially post-laser. It is important therefore to ensure proper:
- Preparation of the skin: Lightening serums or creams can be used before laser treatments to reduce the chance of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Laser settings: Before treatment, it is crucial to choose a laser setting that is appropriate for the targeted skin type. Other settings to consider include the use of skin cooling during laser, laser intensity levels, and the need for smaller laser spot sizes to minimise the effects of the laser on the surrounding skin.
- Post-laser treatment: After any type of laser skin resurfacing treatment, the proper creams, including sunscreens must be used.
Due to the higher risks associated with laser treatments on darker skin types, patients with Asian, olive or dark skin may consider the Cosmelan Peel Program. A consultation is required to determine which treatment is most suitable for your skin and pigmentation type.
FAQ
Can pigmentation be removed?
Existing pigmentation can be removed using different treatments, depending on the type of pigmentation. The Fraxel laser can be used to remove or minimise some types of sun damage, while chemical peels can be used for post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or treating melasma. IPL is a also viable treatment for the reduction of pigmentation, and also improves skin quality.
Pigmentation can also be minimised by using high SPF every day and regularly exfoliating your skin for improved skin cell turnover rates. You can also incorporate pigment-reducing and vitamin B skincare products into your daily routine to reduce the appearance of existing pigmentation.
How long will it take for me to see results after pigmentation treatments?
You should begin to see results after your first treatment, but this will also depend on your specific treatment plan as well as your skin’s level of resistance to the procedure.
You will not see full results until after you’ve had all of the treatments in your plan.
Is pigmentation removal treatment suitable for pregnant or breastfeeding women?
Treatments to remove or lighten pigmentation are not suitable for pregnant or breastfeeding women. There are pregnancy safe skincare products that can be used to reduce and fade pigmentation.
How do I prepare for pigmentation removal?
For two weeks prior to your pigmentation treatment, you should avoid getting a spray tan, being in a tanning booth, or getting excessive sunlight. You should also avoid waxing your face.
Immediately before your treatment, you should thoroughly cleanse your face. Our practitioners will discuss any other necessary preparations with you in your initial consultation as this will vary depending on which treatment you have having.
Is there any downtime required?
Downtime will vary depending on which laser or chemical peel treatment you have for pigmentation. With most laser and chemical peel treatments, you should be able to return to normal activities very soon after treatment, but this will depend on which treatment you receive. Some chemical peel and laser treatments are more intensive and will require anywhere from 1 to 2 weeks of downtime.
Regardless of which treatment you have, you should avoid direct sun exposure, strenuous exercise, skincare with active ingredients and direct heat for 7 days after treatment.
Where to get skin pigmentation treatment in Melbourne?
At the Victorian Cosmetic Institute, our practitioners will carefully assess your pigmentation and formulate a personalised treatment plan for you. We have a wide range of treatment options available and can provide a treatment solution to suit your skin.
Our practitioners are also highly experienced in laser treatments and chemical peels, and will be able to give you the tailored advice for your treatment. We will make sure you understand exactly what will happen and what to expect before any treatment, as well as guide you through the post-treatment process.
Consultations are required prior to any treatment. Get started today by booking online. You can also call our friendly customer care team on 1300 863 824 to arrange your consultation appointment.