Gynaecomastia Surgery Melbourne
Gynaecomastia is an enlargement of the male chest area due to hormonal imbalances. At Victorian Cosmetic Institute, Dr Gavin Chan, (MBBS, General Registration MED0001175745), provides gynaecomastia consultations and surgery where the enlargement is from fat deposits in the chest area.
Male breast gynaecomastia
Male breast gynaecomastia (also spelt gynecomastia) refers to the enlargement of glandular breast tissue in males. Gynaecomastia can occur due to hormonal imbalances, specifically an increase in estrogen levels relative to testosterone levels. This can be physiological (normal) or can be, less commonly, pathological. Pathological causes of gynaecomastia include; Klinefelter’s syndrome, cirrhosis of the liver, testicular tumours, prolactin excess, or are medication related. Gynaecomastia can develop during infancy, adolescence, or later in life, and it may affect one or both breasts.
What is involved in the treatment of gynaecomastia?
A medical consultation with a doctor is required to assess the cause of the enlarged male chest and plan an appropriate treatment;
- A detailed medical history is taken and the chest area is physically examined
- Standardised clinical photos are taken
- Blood tests are ordered, including hormone levels. CT scan, ultrasound, or ultrasound-guided biopsy may be requested, if required
- A liposuction surgery plan is discussed, including the risks and potential side effects of surgery
- The total cost for surgery, inclusive of surgeon fee, anaesthetist fee and hospital fee are provided
- A second consultation will be required prior to surgery to review and sign the consent forms, review the surgical plan and discuss the risks, benefits and potential side effects of surgery. During this second consultation we are able to schedule a surgery date with the hospital.
- Adequate time is allowed to pass (cooling-off period) before the surgery is performed
Dr. Gavin Chan offers consultations for gynaecomastia and male chest fat liposuction surgery at our Templestowe and Berwick clinic locations. A referral from your GP is required for all surgical consultations.
Phone 1300 863 824 to schedule your consultation appointment.
Gynaecomastia causes
There are several potential causes of gynaecomastia, including:
- Hormonal imbalances: Changes in hormone levels, such as decreased testosterone or increased estrogen, can lead to gynaecomastia. This imbalance can occur naturally during puberty, ageing, or as a result of certain medical conditions or medications.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antiandrogens, anabolic steroids, some antidepressants, and medications used to treat prostate conditions or cancer, can contribute to the development of gynaecomastia.
- Health conditions: Conditions that affect hormone levels, such as hypogonadism, hyperthyroidism, liver disease, kidney failure, or tumors of the pituitary gland or adrenal glands, can increase the risk of gynaecomastia.
- Lifestyle factors: Excessive alcohol consumption, use of recreational drugs, and obesity can also increase the risk of developing growth in the chest area.
If male chest enlargement is not due to enlargement of glandular tissue, but instead it is due to accumulation of fat only, it is called pseudo-gynaecomastia, and usually does not have any underlying medical pathology.
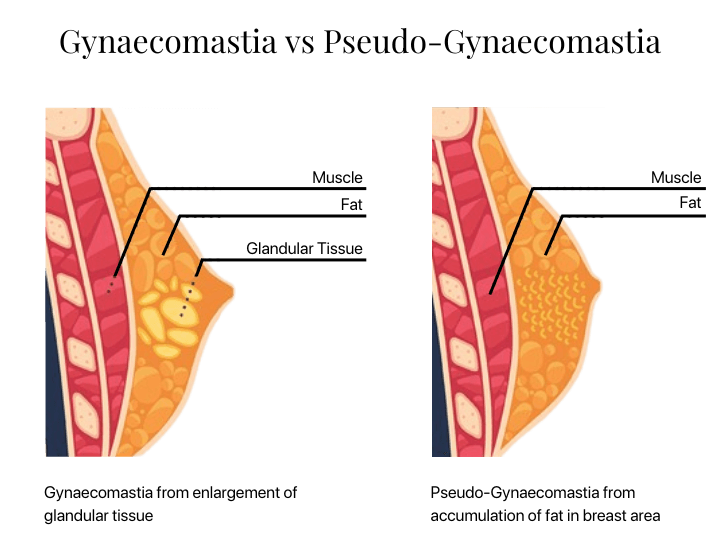
Determine if it is gynaecomastia or fat
To determine whether it is gynaecomastia or excess fat, a doctor will need to first take a history from you. Most people who have gynaecomastia are asymptomatic, however, symptoms such as; nipple discharge, loss of peripheral vision, sexual dysfunction, and infertility, may indicate an underlying hormonal disturbance and possible cause of the gynaecomastia. A family history of gynaecomastia may also be common in those with this condition.
An examination of your chest to determine the consistency of the chest tissue by your doctor is also important in determining whether your problem is due to gynaecomastia (glandular tissue) or whether it is fat. Usually, a series of blood tests (including hormone levels) are then performed. Finally, a CT scan, ultrasound, or ultrasound-guided biopsy may be requested to determine the nature of the tissue present.
Gynaecomastia surgery
Liposuction is a surgical procedure used to treat gynaecomastia by removing excess fat tissue from the male breast area. Liposuction for gynaecomastia involves making small incisions through which a thin tube, called a cannula, is inserted to suction out fat cells.
While liposuction can address gynaecomastia caused by excess fatty tissue, it may not be suitable for cases where the enlargement is primarily due to glandular tissue. Glandular tissue is a firmer type of breast tissue that liposuction cannot adequately remove. In such cases, a different surgical approach, such as direct excision of the glandular tissue, may be necessary to achieve the desired reduction in breast size.
Prior to undergoing liposuction for gynaecomastia, patients undergo a thorough evaluation to determine the most appropriate treatment approach based on the underlying cause and characteristics of their condition.
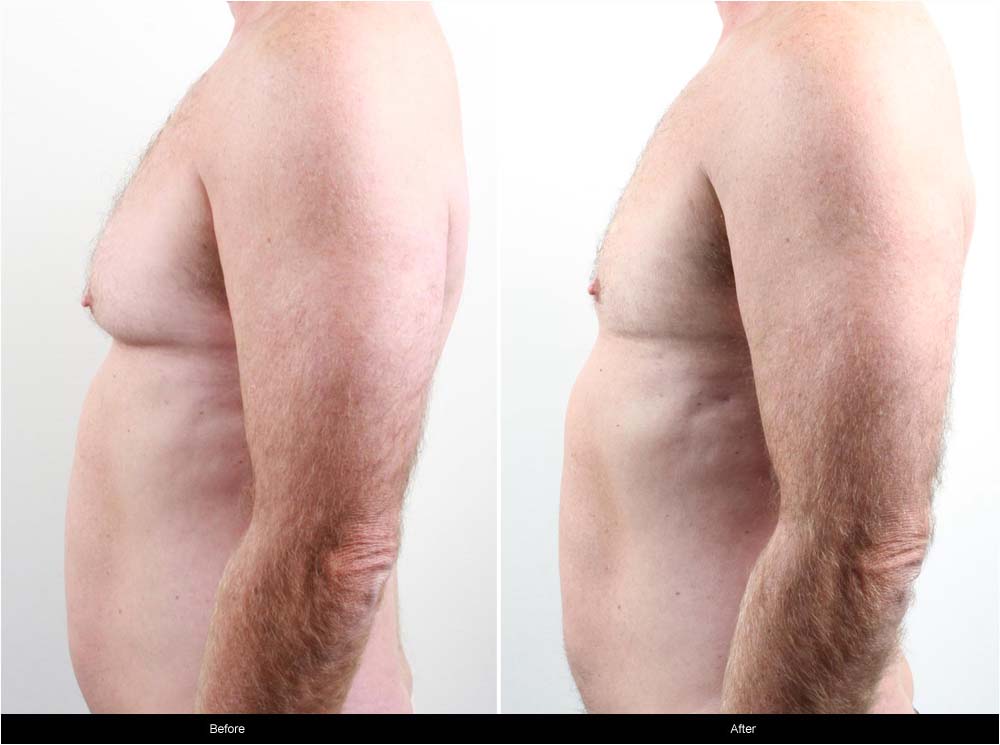
Gynaecomastia Before and After Case Study 1
This man presented to the Victorian Cosmetic Institute wanting to reduce his chest size. He had noticed an enlargement of his chest area since his teenage years, and despite dieting and exercising, he has been unable to reduce the size of his chest.
Blood tests showed no underlying hormonal imbalances or abnormalities, and a chest ultrasound showed only fatty tissue contributing to his concern.
He opted to have liposuction to reduce the size of his chest. The following shows the photos before and one month after liposuction.
The result below is only relevant for this patient and does not necessarily reflect the results other patients may experience. The outcome of each procedure cannot be guaranteed, and individual results may vary due to many factors including the individual’s genetics, diet and exercise. Patient consent has been obtained to display these images.
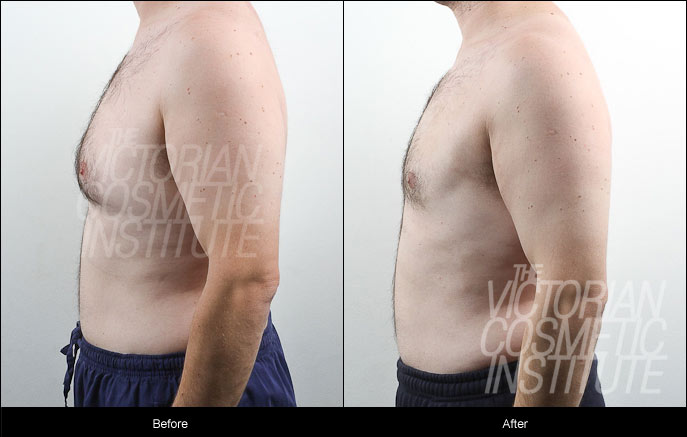
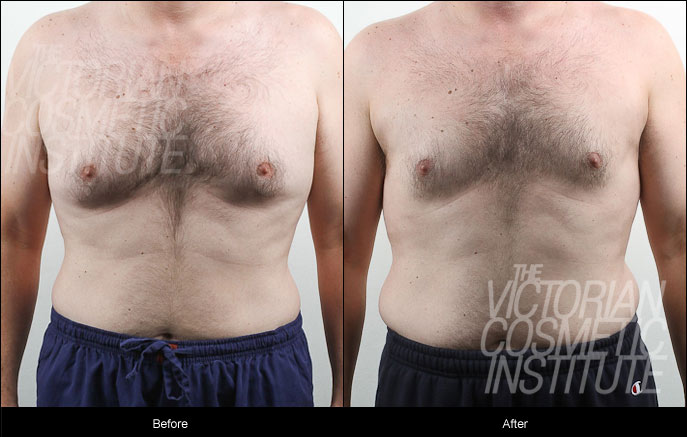
Gynaecomastia Before and After Case Study 2
This man presented to the Victorian Cosmetic Institute wanting to reduce the size of his chest – something he reported he was unable to do despite his dieting and exercising.
Prior to treatment, blood tests and ultrasound were all found to be normal, indicating no hormonal imbalance or other contributing factors which would exclude liposuction as a treatment option.
He underwent liposuction surgery with Dr Gavin Chan to treat his gynaecomastia.
The result below is only relevant for this patient and does not necessarily reflect the results other patients may experience. The outcome of each procedure cannot be guaranteed, and individual results may vary due to many factors including the individual’s genetics, diet and exercise. Patient consent has been obtained to display these images.
Should I worry about gynaecomastia?
Gynaecomastia is a condition that is usually brought about by an imbalance of hormones in the body. This can be from a higher than normal ratio or female to male hormones and the cause of this needs to be investigated. The cause of this imbalance may be due to abnormal hormone secreting tumours, or a congenital imbalance of hormones, or an imbalance due to medications taken – including anabolic steroids, particular diuretics, digoxin (a cardiac drug), and some prostate/hair-loss reduction medication. It is important to find the underlying cause of gynaecomastia, rather than to simply treat this as a cosmetic problem.
If, after appropriate investigations, there is no evidence of glandular tissue and only fat is present, then it can be treated as a cosmetic matter.
Risks and side effects of gynaecomastia surgery
Liposuction is a common surgical procedure used to treat gynaecomastia by removing excess fat tissue from the breast area in males. While it can be a solution for many patients, it’s important to be aware of the potential risks associated with gynaecomastia surgery.
- Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection at the incision sites. Proper post-operative care and adherence to the post treatment instructions can help minimise this risk.
- Bleeding and hematoma: Liposuction involves the insertion of a cannula to suction out fat cells, which can result in bleeding. In some cases, this bleeding can lead to the formation of a hematoma (a collection of blood under the skin), which may require additional treatment.
- Changes in skin sensation: Some patients may experience temporary or permanent changes in sensation, such as numbness or tingling, in the treated area.
- Irregular contours: There is a risk of uneven or irregular results, particularly if too much or too little fat is removed.
- Fluid accumulation: Following liposuction, fluid may accumulate in the treated area, leading to swelling and discomfort. Draining the fluid may be necessary to alleviate these symptoms.
- Scarring: There is a risk of scarring at the incision site, particularly if proper wound care is not maintained or if the patient has a history of hypertrophic or keloid scarring.
- Anaesthesia risks: Liposuction is performed under general anaesthesia which carries its own risks, including allergic reactions and complications related to the administration of anaesthesia.
It’s important for patients considering liposuction for gynaecomastia to discuss their concerns and medical history with their doctor, and for the doctor to ensure the patient is informed about the potential risks, benefits and side effects of the procedure.
How do I treat gynaecomastia or chest fat?
Firstly, the underlying cause of gynaecomastia must be treated. An endocrinologist (a hormone specialist) may need to do this. Male chest enlargement without glandular tissue does not need to be investigated further.
Once the underlying cause has been determined and reversed if needed, cosmetic treatment can commence.
One treatment for male gynaecomastia, and this is surgery. Surgery will require an incision around the nipple to allow access to the tissue so it can be removed.
Alternatively, treatment of the underlying hormonal problem can often resolve gynaecomastia, and this can sometimes be done with medication. Liposuction cannot be used to remove glandular tissue from the chest as the liposuction cannula ports are too fine to suction the glandular tissue. Liposuction and glandular tissue removal can often be done in the same procedure.
FAQs
Will gynaecomastia go away?
In some cases, gynaecomastia may resolve on its own without the need for treatment, particularly if it occurs during puberty. During adolescence, hormonal fluctuations can lead to temporary breast tissue enlargement in some boys, which typically resolves within a few months to a couple of years as hormone levels stabilise.
However, gynaecomastia that persists beyond puberty or develops later in life may not resolve spontaneously. The likelihood of gynaecomastia going away depends on various factors, including the underlying cause, the individual’s age, and their overall health.
For example, if gynaecomastia is caused by certain medications, discontinuing the medication may lead to a reduction in breast tissue over time. Similarly, if the condition is related to lifestyle factors such as obesity or excessive alcohol consumption, making changes to improve overall health and lifestyle habits may help reduce the size of the male breasts.
In cases where gynaecomastia does not resolve on its own, medical treatment or surgical intervention may be necessary if the patient wishes to address the condition. Treatment options may include hormone therapy, medication to reduce breast tissue, or surgical procedures such as liposuction or glandular tissue removal.
How much does gynaecomastia surgery cost?
The cost of surgery consists of the surgeon’s fee, the anaesthetist fee and the hospital fee. Pricing for surgery varies and will be discussed during your consultation appointment.
What is gynaecomastia surgery?
Gynaecomastia surgery, or male breast reduction surgery (reduction mammaplasty), removes excess tissue from the male chest.
Do I need a referral for gynaecomastia (male breast reduction) surgery?
Patients seeking cosmetic surgery will require a referral from a GP or other medical specialist. For the referral to be valid, the GP or other referring practitioner must not provide cosmetic surgery or non-surgical cosmetic procedures themselves.
Why should I choose Victorian Cosmetic Institute for gynaecomastia surgery?
Dr. Gavin Chan (MBBS, General Registration MED0001175745) at Victorian Cosmetic Institute will assess and investigate first whether the chest enlargement is caused by gynaecomastia or fat deposits. Knowing this information is crucial in determining whether the enlarged chest can be treated with liposuction surgery. Any pathology or other tests will be ordered as required to help determine the cause of the enlarged male chest.
Contact our friendly Customer Care team on 1300 863 824 to schedule your initial consultation for male breast reduction.
Last updated July 2024
